Community Articles
- Cloudera Community
- Support
- Community Articles
- AutoScaling MiNiFi On Kubernetes
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
Created on 08-14-2019 06:45 PM - edited 08-17-2019 02:09 PM
MiNiFi (Java Version) is essentially NiFi with a few differences and hence why it runs so darn well on containers/Kubernetes. The use case is to have a single management console (Edge Flow Manager) to manage 0 + many MiNiFi agents which require autoscaling on Kubernetes based on some arbitrary metrics...for example CPU/RAM threshold. EFM and NiFi Registry are required but don't need autoscaling; therefore, these services will be deployed on Azure Container Service. MiNiFi on the other hand often benefits from autoscaling and hence it will be deployed on Azure Kubernetes Service.
Required for this demonstration
- Azure subscription
- Container Registry
- Demo will leverage Azure Container Registry
- Kubernetes Service
- Demo will leverage Azure Kubernetes Service
- Azure CLI
- The following images need to be stored in Azure Container Registry
- Edge Flow Manager
- NiFi Registry
- MiNiFi (Java)
- https://github.com/sunileman/CEM1.0-Java-MiNiFi
- This image will come precooked with Azure/AWS NARs
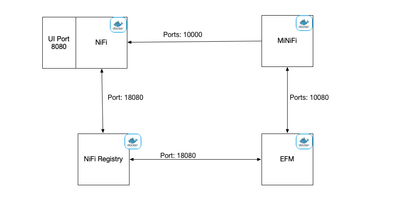
Architecture
This is a 10k foot view of the architecture. EFM communicates with MiNiFi agents about the work they need to do. EFM also communicates with NiFi Registry to store/version control flows will get passed to the MiNiFi agents.
Deploy NiFi Registry and EFM on Azure Container Service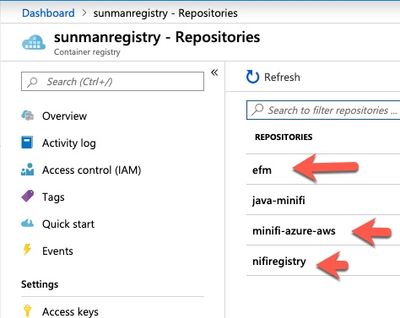
Since EFM and Registry don't really benefit from autoscaling, they both are great fit for Azure container service (Mostly Static installs). ACS will guarantee EFM and NiFi registry are alway up with 1 container instance each. EFM, MiNiFi, and Registry have all been imported into my container registry on azure.
Create NiFi Registry on ACS
NiFi Registry variables to note
- --name
- Name of the nifi registry container
- --dns-name-label
- Prefix for the dns on the registry service. This will be used as an input into EFM container environment variable
az container create --resource-group sunmanCentralRG --name mynifiregistry --image sunmanregistry.azurecr.io/nifiregistry:latest --dns-name-label nifiregistry --ports 18080 --registry-username ****** --registry-password ******
Create EFM on ACS
EFM variables to note
- --NIFI_REGISTRY should match NiFi registry Container DNS (fully qualified server name)
- --dns-name-label
- DNS prefix
az container create --resource-group sunmanCentralRG --name efm --image sunmanregistry.azurecr.io/efm:latest --dns-name-label myefm --ports 10080 --registry-username ***** --registry-password **** --environment-variables 'NIFI_REGISTRY_ENABLED'='true' 'NIFI_REGISTRY_BUCKETNAME'='testbucket' 'NIFI_REGISTRY'='http://mynifiregistry.centralus.azurecontainer.io:18080'
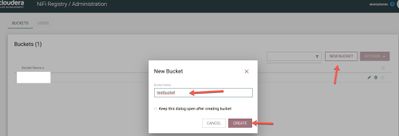
Create a 'testbucket' on NiFi Registry
MiNiFi flows will be designed using EFM and stored in the NiFi Registry bucket 'testbucket'. This bucket name was identified as a variable during EFM container was creation.
'NIFI_REGISTRY_BUCKETNAME'='testbucket'
NiFi registry will be available under
YourNiFiRegistryDSN:18080/nifi-registry/ . For example http://mynifiregistry=y.centralus.azurecontainer.io:18080/nifi-registry/
- Click on "NEW BUCKET",
- Enter bucket name - testbucket
- Click create
Validate EFM is up
EFM UI will be available under
http://YourEfmDnsPrefix.centralus.azurecontainer.io:10080/efm/ui for example http://myefm.centralus.azurecontainer.io:10080/efm/ui
Run MiNiFi Kubernetes Deployment
The easiest way to run a deployment in k8s is to build a manifest file. To learn more about k8s manifest files here. Look for < > in the manifest below, as these are the variables a change prior to your deployment (only a few, super simple).
Variable to Note
- MINIFI_AGENT_CLASS
- This will be the agent class published to EFM. To learn more about EFM, go here
Kubernet Manifest File:
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: minifi spec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: minifi template: metadata: labels: app: minifi spec: containers: - name: minifi-container image: <Your Containe Registry>/minifi-azure-aws:latest ports: - containerPort: 10080 name: http - containerPort: 6065 name: listenhttp - containerPort: 22 name: ssh resources: requests: cpu: ".05" memory: "1Gi" limits: cpu: "1" env: - name: NIFI_C2_ENABLE value: "true" - name: MINIFI_AGENT_CLASS value: "test" - name: NIFI_C2_REST_URL value: "http://<Your EFM servername>.centralus.azurecontainer.io:10080/efm/api/c2-protocol/heartbeat" - name: NIFI_C2_REST_URL_ACK value: "http://<Your EFM servername>.centralus.azurecontainer.io:10080/efm/api/c2-protocol/acknowledge" --- kind: Service #+ apiVersion: v1 #+ metadata: #+ name: minifi-service #+ spec: #+ selector: #+ app: minifi #+ ports: #+ - protocol: TCP #+ targetPort: 10080 #+ port: 10080 #+ name: http #+ - protocol: TCP #+ targetPort: 22 #+ port: 22 #+ name: ssh #+ - protocol: TCP #+ targetPort: 6065 #+ port: 6065 #+ name: listenhttp #+ type: LoadBalancer #+
Once the manifest file has been updated, store it as minifi.yml (this can be any name). Deploy on k8s using
kubectl apply -f minifi.yml
output
sunile.manjee@hwx:~/Documents/GitHub/AKS-YAMLS(master:high_voltage:) » kubectl apply -f minifi.yml deployment.extensions/minifi created service/minifi-service created sunile.manjee@hwx:~/Documents/GitHub/AKS-YAMLS(master:high_voltage:) »
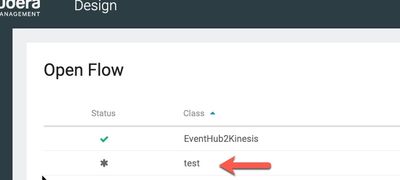
MiNiFi has been successfully deployed. To verify successful deployment visit EFM. EFM should show the agent class name 'test' matching the class name used in the minifi k8s manifest file.
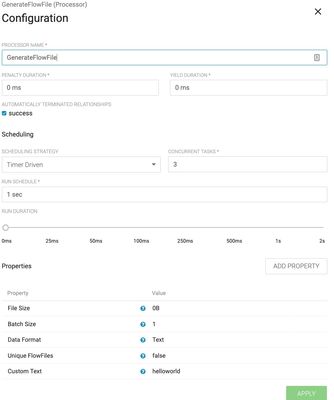
Open the class and design any flow. Here I simply used GenerateFlowFile and terminated success relationship with 3 concurrent threads
Click on publish and soon thereafter MiNiFi will be executing the flow.
AutoScale MiNiFi
At this time a single MiNiFi container/agent is executing flows. I purposefully set MiNiFi CPU allocation (manifest file) to a small number to force the autoscaling.
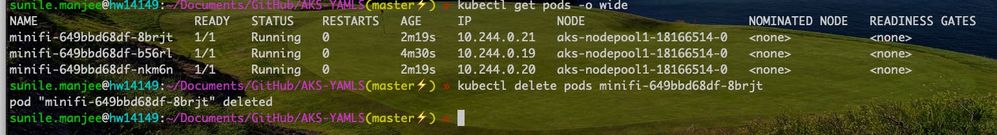
First lets check the number of minifi pods running on k8s
Single MiNiFi pod. Lets check if autoscaling is enabled for this deployment
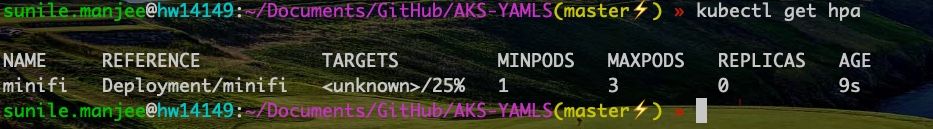
To enable autoscaling on k8s:
kubectl autoscale deployment minifi --cpu-percent=25 --min=1 --max=3
minifi is the deployment name. If CPU utilization exceeds 25%, the autoscaler increases the pods up to a maximum of 3 instances. A ...
Verify autoscaling is enabled on the minifi deployment
Number of minifi pods after autoscaling was enabled (3).
Kubernetes added 2 additional MiNiFi pods. Lets kill one of the pods and see what happens
Kubernetes immediately launched a new MiNiFi container after a MiNiFi pod was killed.
Enjoy AutoScale on MiNiFi!