Community Articles
- Cloudera Community
- Support
- Community Articles
- Ingest Remote Camera Images from Raspberry Pi via ...
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
Created on 01-15-2017 05:42 PM - edited 09-16-2022 01:38 AM
Raspberry PIs and other small devices often have cameras or can have camera's attached. Raspberry Pi's have cheap camera add-ons that can ingest still images and videos (https://www.raspberrypi.org/products/camera-module/). Using a simple Python script we can ingest images and then ingest them into our central Hadoop Data Lake. This is a nice simple use case for Connected Data Platforms with both Data in Motion and Data at Rest. This data can be processed in-line with Deep Learning Libraries like TensorFlow for image recognition and assessment. Using OpenCV and other tools we can process in-motion and look for issues like security breaches, leaks and other events.
The most difficult part is the Python code which reads from camera, adds a watermark, converts to bytes, sends to MQTT and then ftps to an FTP server. I do both since networking is always tricky. You could also add if it fails to connect to either, store to a directory on a mapped USB drive. Once network returns send it out, it would be easy to do that with MiniFi which could read that directory.
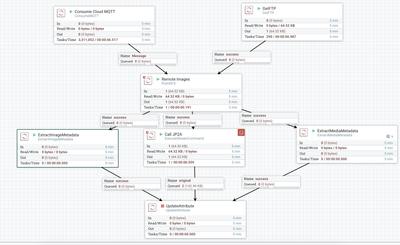
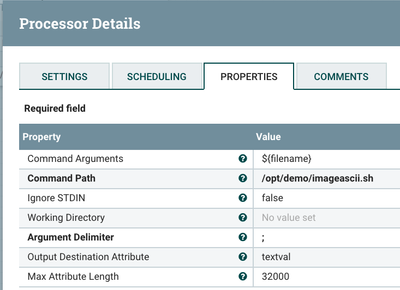
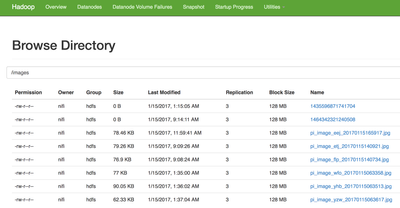
Once the file lands into the MQTT broker or FTP server, NIFI pulls it and bring it into the flow. I first store to HDFS for our Data @ Rest permanent storage for future deep learning processing. I also run three processors to extra image metadata and then call jp2a to convert the image into an ASCII picture.
ExecuteStreamCommand for Running jp2a
The Output Ascii
HDFS Directory of Uploaded Files
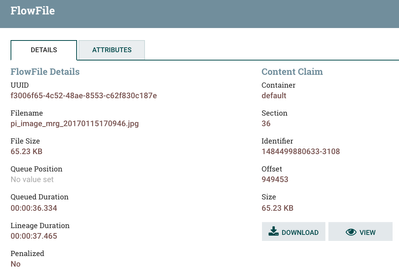
Metadata extracted from the image
An Example Imported Image
Other Meta Data
Meta Data Extracted
A Converted JPG to ASCII
Running JP2A on Images Stored in HDFS via WebHDFS REST API
/opt/demo/jp2a-master/src/jp2a "http://hdfsnode:50070/webhdfs/v1/images/$@?op=OPEN"
Python on RPI
#!/usr/bin/python
import os
import datetime
import ftplib
import traceback
import math
import random, string
import base64
import json
import paho.mqtt.client as mqtt
import picamera
from time import sleep
from time import gmtime, strftime
packet_size=3000
def randomword(length):
return ''.join(random.choice(string.lowercase) for i in range(length))
# Create unique image name
img_name = 'pi_image_{0}_{1}.jpg'.format(randomword(3),strftime("%Y%m%d%H%M%S",gmtime()))
# Capture Image from Pi Camera
try:
camera = picamera.PiCamera()
camera.annotate_text = " Stored with Apache NiFi "
camera.capture(img_name, resize=(500,281))
pass
finally:
camera.close()
# MQTT
client = mqtt.Client()
client.username_pw_set("CloudMqttUserName","!MakeSureYouHaveAV@5&L0N6Pa55W0$4!")
client.connect("cloudmqttiothoster", 14162, 60)
f=open(img_name)
fileContent = f.read()
byteArr = bytearray(fileContent)
f.close()
message = '"image": {"bytearray":"' + byteArr + '"} } '
print client.publish("image",payload=message,qos=1,retain=False)
client.disconnect()
# FTP
ftp = ftplib.FTP()
ftp.connect("ftpserver", "21")
try:
ftp.login("reallyLongUserName", "FTP PASSWORDS SHOULD BE HARD")
ftp.storbinary('STOR ' + img_name, open(img_name, 'rb'))
finally:
ftp.quit()
# clean up sent file
os.remove(img_name)
References:
- https://community.hortonworks.com/repos/77987/rpi-picamera-mqtt-nifi.html?shortDescriptionMaxLength=...
- https://github.com/bikash/RTNiFiStreamProcessors
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/37499739/how-can-i-send-a-image-by-using-mosquitto
- https://www.raspberrypi.org/learning/getting-started-with-picamera/worksheet/
- https://www.cloudmqtt.com/
- https://developer.ibm.com/recipes/tutorials/sending-and-receiving-pictures-from-a-raspberry-pi-via-m...
- https://developer.ibm.com/recipes/tutorials/displaying-image-from-raspberry-pi-in-nodered-ui-hosted-...
- https://www.raspberrypi.org/learning/getting-started-with-picamera/worksheet/
- https://github.com/jpmens/twitter2mqtt
- http://www.ev3dev.org/docs/tutorials/sending-and-receiving-messages-with-mqtt/
- https://github.com/njh/mqtt-http-bridge
- https://www.raspberrypi.org/learning/parent-detector/worksheet/
- http://picamera.readthedocs.io/en/release-1.10/recipes1.html
- http://picamera.readthedocs.io/en/release-1.10/faq.html
- http://www.eclipse.org/paho/
- http://picamera.readthedocs.io/en/release-1.10/recipes1.html#capturing-to-an-opencv-object
- https://github.com/cslarsen/jp2a
- https://www.raspberrypi.org/learning/getting-started-with-picamera/
- https://www.raspberrypi.org/learning/tweeting-babbage/worksheet/
- https://csl.name/jp2a/