Community Articles
- Cloudera Community
- Support
- Community Articles
- PySpark with Livy via script submission and Zeppel...
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
Created on
03-17-2017
03:44 PM
- edited on
02-27-2020
05:30 AM
by
VidyaSargur
This tutorial will demonstrate how to execute PySpark jobs on an HDP cluster and pass in parameter values using the Livy REST interface. I will also demonstrate how to interact with Livy via Apache Zeppelin and use forms in Zeppelin to pass in parameter values. Livy is an open source REST interface for interacting with Spark.
- Livy requires at least Spark 1.6.
- By default, Livy is built against Apache Spark 1.6.2 with HDP 2.5.3
- If on HDP 2.4.2, then Livy 0.2.0 might be part of HDP 2.4.2 repos. If not, then it can be cloned from: https://github.com/cloudera/livy
- Livy is built against Apache Spark 1.6.2 with HDP 2.5.3.
- The following was tested with HDP 2.5.3 and Spark 1.6.2.
Business Use Case:
A PySpark script that resides on the Livy server aggregates order statistics from a Hive table for a date range passed in as parameters to the Python script.
The Start and End dates are passed in as parameter values to the Python script.
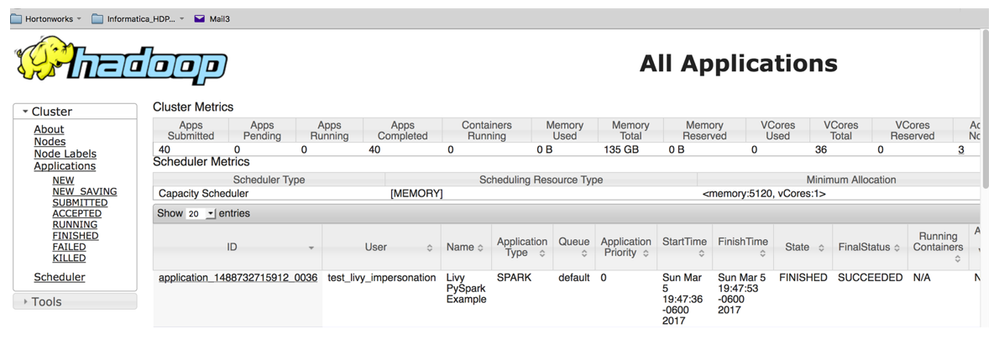
The job runs on the cluster via YARN and produces the following output:
| Start Date | End Date | City | Min Order Amt | Max Order Amt | Avg Order Amt |
| 2017-02-06 | 2017-02-15 | Chicago | 54.23 | 788.23 | 354.23 |
| 2017-02-06 | 2017-02-15 | San Francisco | 98.23 | 1032.12 | 634.12 |
Users can execute the PySpark script via Livy using curl from a terminal window, Apache Zeppelin, or other applications.
Execute PySpark script on HDP cluster via Livy using curl
from pyspark import SparkContext, HiveContext
import sys
sc = SparkContext('yarn-client')
spark = HiveContext(sc)
start_date=sys.argv[1]
end_date=sys.argv[2]
sql = """
select '%s' start_date, '%s' as end_date, city, min(order_amt) as min_order_amount, max(order_amt) as max_order_amount, avg(order_amt) as average_order_amount from orders where
to_date(order_date) between '%s' and '%s' group by city order by city
""" %(start_date,end_date,start_date,end_date)
spark.sql(sql).show()
How to call PySpark Script:
- The PySpark script is a regular file on the Livy server. Notice I’m setting the location of the file with ‘file:’
- Livy allows for impersonation to create a shell running as a different user. This is the setting ‘proxyUser’. Notice that I’m running the script as ‘test_livy_impersonation’
- All the properties supported by Spark such as the number of executors, number of cores, executor memory, etc., can be changed at session creation. Their format is the same as when executing via spark-submit. Notice that I’m setting the number of executor cores to 4.
- I’m passing parameters to the script by setting values for ‘args’
Command to run script:
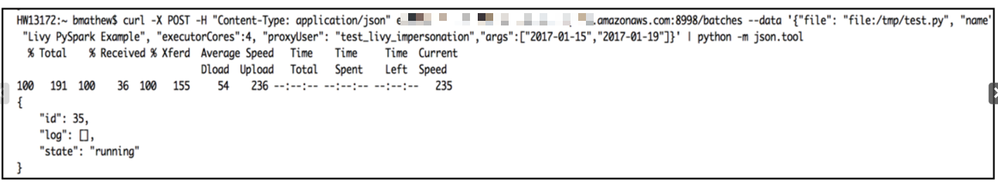
curl -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json"ec2-xxxxxx.compute.amazonaws.com:8998/batches --data '{"file": "file:/tmp/test.py", "name": "Livy PySpark Example", "executorCores":4, "proxyUser": "test_livy_impersonation","args":["2017-01-15","2017-01-19"]}' | python -m json.tool
*Note: The default Livy port will be 8998
After executing the above command, you will get the following output which gives you the session ID number:
Get output:
Depending on the complexity of processing and availability of resources on the cluster, the job completion could take some time.
Take the session ID from the output above (33) and run the following command to get the results from the log file:
curl ec2-xxxxxx.us-east-2.compute.amazonaws.com:8998/batches/35/log | python -m json.tool
*Note: Replace 35 above with your session ID
Results from the log file:
Zeppelin with Livy and pass in parameter values via Zeppelin forms
At a minimum, configure Zeppelin’s Livy server interpreter and set ‘zeppelin.livy.url’ to your Livy server:
Also, set livy.spark.master to YARN if you want jobs to run on YARN:
If your cluster is Kerberized, then you will need to set values for ‘zeppelin.livy.keytab’ and ‘zeppelin.livy.principal’:
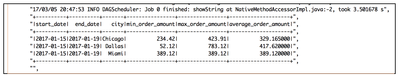
Sample output from my Hive table using Spark Sql interpreter (%sql):
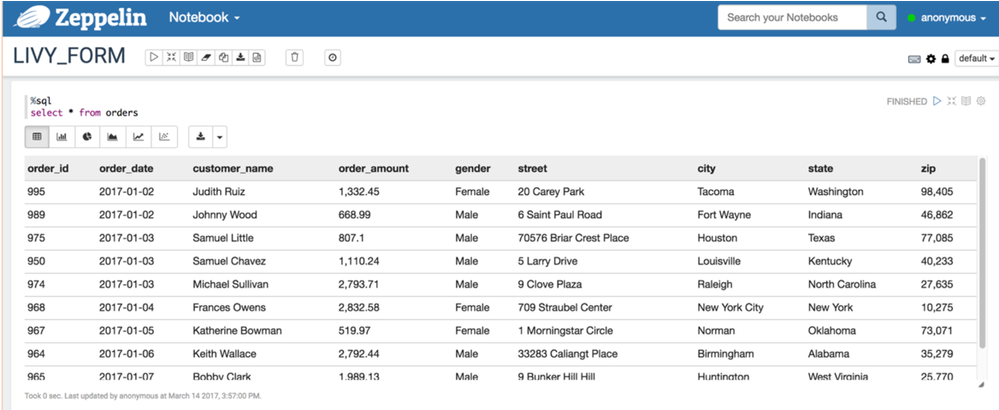
You can access the data in this Hive table using PySpark via the Livy interpreter (%livy.pyspark) with input forms that pass parameter values to your PySpark script:
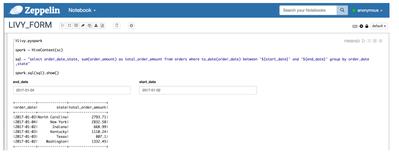
- In your PySpark code enclose parameters with ‘${parameter_name}’. In the example below I am passing in start date and end date as {$start_date} and ${end_date}.
- Input boxes will appear to enter values
This also works with the Spark SQL (%sql) interpreter: