Community Articles
- Cloudera Community
- Support
- Community Articles
- Remove a host from Cloudera Manager and add it to ...
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
Created on
09-05-2021
11:36 PM
- edited on
09-06-2021
02:58 AM
by
subratadas
Summary of the article
I have encountered issues of the following scenario several times:
A customer removes a host from a cluster managed by Cloudera Manager and adds the host to another cluster managed by Cloudera Manager. At this time, problems often occur.
These problems are often caused by the old cluster files remaining on the host, and these old files cause the new Cloudera Manager to be unable to control the host normally.
So I verified what files will be generated on a host after adding it to a CDP cluster managed by Cloudera Manager.
In other words, after removing a host from Cloudera Manager, what files do we need to delete manually?
Introduction to the Test environment
CDP Runtime version: CDP PvC Base 7.1.6
CM version: Cloudera Manager 7.3.1
Whether to enable Kerberos: Yes
Whether to enable TLS: Yes
Auto-TLS: Yes
Auto-TLS Use Case: Use Case 1 - Using Cloudera Manager to generate an internal CA and corresponding certificates (Refer to Configuring TLS Encryption for Cloudera Manager Using Auto-TLS)
Experimental steps
After adding a host named c3669-temp-node1.kyanlab.cloudera.com to the cluster c3669, I added the YARN Node Manager role to this host, and then I used the following command to find the newly added files in the host:
find /usr -type d -iname '*cloudera*'
find /var -type d -iname '*cloudera*'
find /etc -type d -iname '*cloudera*'
find /opt -type d -iname '*cloudera*'
- I found that because I chose to install the OpenJDK provided by Cloudera Manager when I added the node, there is this OpenJDK on this newly added node: /usr/java/jdk1.8.0_232-cloudera.
- I found some YUM-related directories under the /var directory, and there are Cloudera Manager Server and Agent-related directories under /var/lib.
- The Cloudera Manager Agent-related directories and YARN-related directories are created under the /etc directory (because I added the Node Manager role).
- Needless to say, the parcel-related directories and some Cloudera Manager-related directories are naturally created in the /opt directory.
- In addition, I found that many alternatives files have been created through the command
ls -AFlh /etc/alternatives | grep -Ei cloudera
Regarding these alternatives files, we can track them as the following steps:
[root@c3669-temp-node1 hadoop-yarn]# which yarn
/usr/bin/yarn
[root@c3669-temp-node1 hadoop-yarn]# ls -AFlh /usr/bin/yarn
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 22 Aug 30 10:18 /usr/bin/yarn -> /etc/alternatives/yarn*
[root@c3669-temp-node1 hadoop-yarn]# ls -AFlh /etc/alternatives/yarn
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 63 Aug 30 10:18 /etc/alternatives/yarn -> /opt/cloudera/parcels/CDH-7.1.6-1.cdh7.1.6.p0.10506313/bin/yarn*
[root@c3669-temp-node1 hadoop-yarn]# alternatives --list | grep -Ei yarn
yarn auto /opt/cloudera/parcels/CDH-7.1.6-1.cdh7.1.6.p0.10506313/bin/yarn
hadoop-conf auto /etc/hadoop/conf.cloudera.yarn
[root@c3669-temp-node1 hadoop-yarn]#
What will happen after removing this new node from Cloudera Manager?
At this point, I can be sure that my Node Manager can run successfully on the new host c3669-temp-node1.kyanlab.cloudera.com.
I refer to this document to remove this node from Cloudera Manager.
Obviously, after deleting the host from Cloudera Manager according to the above document, any files on Node will not actually be deleted. Those files created in /usr/, /var/, /opt/, etc. still remain on this host.
Next, what files do we need to delete manually?
First of all, we definitely need to delete the software installed by the Cloudera Manager repo.
Of course, if you plan to add this node to another CDP of the same version, you can omit this step.
# yum repolist | grep -Ei cloudera
cloudera-manager Cloudera Manager, Version 7.3.1 6# yum repo-pkgs cloudera-manager list
Loaded plugins: fastestmirror
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile
* base: mirrors.radwebhosting.com
* epel: mirror.prgmr.com
* extras: mirror.sfo12.us.leaseweb.net
* updates: sjc.edge.kernel.org
Installed Packages
cloudera-manager-agent.x86_64 7.3.1-10891891.el7 -manager
cloudera-manager-daemons.x86_64 7.3.1-10891891.el7 -manager
openjdk8.x86_64 8.0+232_9-cloudera -manager# yum repo-pkgs cloudera-manager remove -y
From the output of the above command, we can find that on my new node, three software have been installed through the Cloudera Manager repo. They are CM Agent, CM daemons and OpenJDK. Use the repo-pkgs remove command to delete these software. Since I plan to add this node to a CDP 7.1.6 cluster of the same version later (by another CM), I will skip this step here.
Update:
I found that these yum packages installed by the cloudera-manager repo still need to be manually deleted. Because when I add the old node to a new cluster, an error occurs during the installation of Cloudera packages. The reason for the error is that when I manually deleted some directories under /usr, /var and /etc, some of these directories were managed by Cloudera packages, so I need to reinstall these packages, and if I don’t delete these packages manually, CM will think that the package on this host does not need to be installed, so the subsequent configuration will fail due to lack of files.
Therefore, whether you plan to add the old host to another cluster of the same version or a different version of the cluster, you need to manually delete the package installed by the cloudera-manager repo first. And the step of deleting package needs to be performed before finding {/usr, /var, /etc...} and deleting related directories.
And, in my environment, "yum repo-pkgs cloudera-manager remove" does not work, so I use a workaround to delete these packages:
clouderaPkgs=`(yum list installed | grep -Ei cloudera | awk '{print $1}')`
for i in ${clouderaPkgs[@]}; do
yum remove -y $i;
done
Now, let us remove the remaining directories created by Cloudera packages:
declare -a dirsSCM
dirsSCM=(`find /var -type d -iname '*cloudera*'`)
for i in ${dirsSCM[@]}; do
echo $i
rm -rf $i
done
dirsSCM=(`find /etc -type d -iname '*cloudera*'`)
for i in ${dirsSCM[@]}; do
echo $i
rm -rf $i
done
dirsSCM=(`find /opt -type d -iname '*cloudera*'`)
for i in ${dirsSCM[@]}; do
echo $i
rm -rf $i
done
Of course, don't forget, it is best to delete the directory /var/run/cloudera-scm-agent, which is used by the CM Agent to manage various role instances (such as DataNode, NodeManger, etc.).
Update: I just found that after a reboot, this directory is gone. It's a tmpfs filesystem.
Then we need to manually clean up the alternatives-related files. This is a bit troublesome, and I have encountered several cases where the customer added the host to a new Cloudera Manager managed cluster and since the old alternatives related files already exist, the new cluster's files will not be propagated correctly.
# ls -AFlh /etc/alternatives | grep -Ei cloudera | awk '{print $9"\t"$NF}' | sed -r 's/\*$//g' > /tmp/alternaives_cloudera_list.txt
# head -n 5 /tmp/alternaives_cloudera_list.txt
avro-tools /opt/cloudera/parcels/CDH-7.1.6-1.cdh7.1.6.p0.10506313/bin/avro-tools
beeline /opt/cloudera/parcels/CDH-7.1.6-1.cdh7.1.6.p0.10506313/bin/beeline
bigtop-detect-javahome /opt/cloudera/parcels/CDH-7.1.6-1.cdh7.1.6.p0.10506313/bin/bigtop-detect-javahome
catalogd /opt/cloudera/parcels/CDH-7.1.6-1.cdh7.1.6.p0.10506313/bin/catalogd
cdsw /opt/cloudera/parcels/CDSW-1.9.1.p1.10118148/scripts/cdsw
# wc -l /tmp/alternaives_cloudera_list.txt
131 /tmp/alternaives_cloudera_list.txt# filter out the alternatives items generated by Cloudera Manager.
ls -AFlh /etc/alternatives | grep -Ei cloudera | awk '{print $9"\t"$NF}' | sed -r 's/\*$//g' > /tmp/alternaives_cloudera_list.txt
# For example, "alternatives --remove yarn /opt/cloudera/parcels/CDH-7.1.6-1.cdh7.1.6.p0.10506313/bin/yarn" will delete this item for yarn generated by Cloudera Manager.
# use a loop to delete all the items.
while read line; do
argsArr=($line);
echo -e "${argsArr[0]}...${argsArr[1]}";
alternatives --remove ${argsArr[0]} ${argsArr[1]};
done < /tmp/alternaives_cloudera_list.txt
So far, I should have cleaned up all the files that need to be manually deleted, so I restarted the host.
Then I created a new CDP 7.1.6 cluster, turned on Kerberos and TLS, and tried to add the host just now.
I deployed a CDP PvC Base 7.1.6 cluster with a one-click deployment script, the CM version is 7.3.1, and the new cluster is named C1669.
Therefore, the CDP version and CM version of this new cluster -- c1669 is the same as the version of the old cluster -- c3669.
After deploying the cluster -- c1669, I used the script to enable Kerberos and TLS. Now the KDC server used by the cluster is located on the host c1669-node1, which is also the host where the CM is located.
Regarding TLS I also used the same Auto-TLS case 1 as the c3669 cluster.
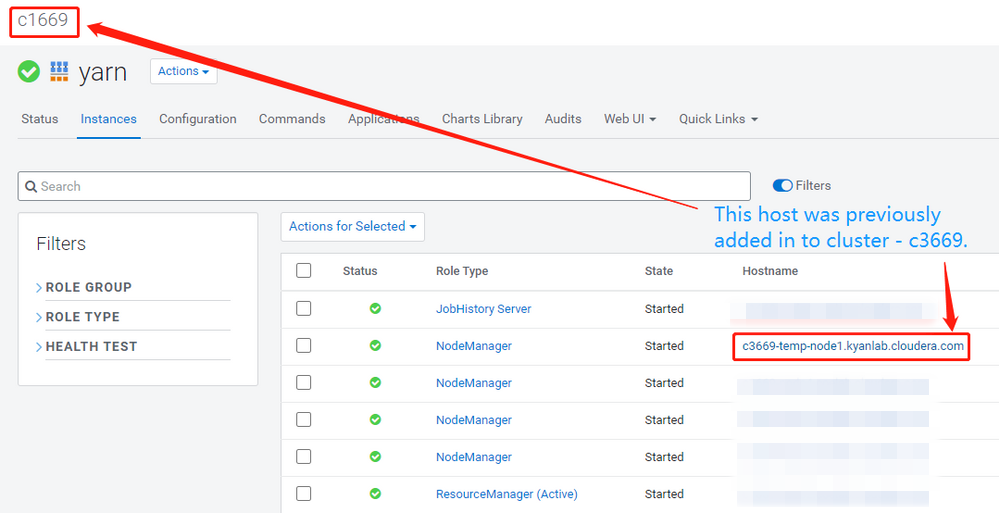
Now I'm adding the host c3669-temp-node1.kyanlab.cloudera.com to the newly created c1669 cluster and try to add a NodeManager role to it to see if it can be successfully started.
As a result, as I expected, the host c3669-temp-node1.kyanlab.cloudera.com was successfully added to the cluster c1669, and the newly deployed Node Manager can be successfully started.
Conclusion
If you need to remove a host from an existing CDP/CDH cluster and add it to another CDP/CDH cluster, please follow the steps below:
- Refer to this document to remove this node from Cloudera Manager.
- Remove the packages which are installed via cloudera-manager repository.
- Delete the remained files created by CM Agent and those packages installed by cloudera-manager.
- Reboot the host.
- Now you can add this host to a new cluster managed by CM.