Community Articles
- Cloudera Community
- Support
- Community Articles
- Spinning up Hadoop HDP cluster on local machine us...
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
Created on 06-15-2016 01:21 AM - edited 08-17-2019 12:03 PM
Often times, maintaining a hadoop cluster for longer periods on cloud is an expensive task. Sometimes engineers might also encounter situations of not having immediate access to cloud environment, in order to quickly spin up their own cluster and play arround. As an easy alternative, vagrant with virtual box as a provider, HDP cluster can be set up on your own laptop.
Step 1 - Install prerequisites
- Download and install from here Vagrant.
- Download and install Oracle VirtualBox as the Vagrant Provider.
Step 2 - Generation of Vagrantfile
Create a working directory for Vagrant file generation and initiating the deployment vis vagrant
$ mkdir hdp22 $ cd hdp22
Following command will generate the Vagrantfile in current directory. This file will define VMs that are to be on the cluster.
$ vagrant init $ vi Vagrantfile
Step 3 - Configuration of VMs in Vagrantfile
Lets configure Vagrant to use CentOS 6.6/ CentOS 6.7 as the base box
$ config.vm.box = "bento/centos-6.7" or $ config.vm.box = "chef/centos-6.6"
The below script should be included in the Vagrantfile to allow some basic provisioning for VMs like
1. Install NTP service
2. Disable firewall, SElinux
3.(Optional) Install wget
$script = <<SCRIPT sudo yum -y install ntp sudo chkconfig ntpd on sudo chkconfig iptables off sudo /etc/init.d/iptables stop sudo setenforce 0 sudo sed -i 's/SELINUX=enforcing/SELINUX=disabled/g' /etc/selinux/config sudo sh -c 'echo "* soft nofile 10000" >> /etc/security/limits.conf' sudo sh -c 'echo "* hard nofile 10000" >> /etc/security/limits.conf' sudo sh -c 'echo never > /sys/kernel/mm/redhat_transparent_hugepage/defrag' sudo sh -c 'echo never > /sys/kernel/mm/redhat_transparent_hugepage/enabled' SCRIPT config.vm.provision "shell", inline: $script
Step 4 - Configure the definition of VMs
The following configurations will define 4 Virtual machines to be used in the HDP cluster,
1 Ambari server
1 Hadoop master
2 slaves
The machines defined have below hostnames:
1. ambari1.mycluster
2. master1.mycluster
3. slave1.mycluster
4. slave2.mycluster
# Ambari1
config.vm.define :ambari1 do |a1|
a1.vm.hostname = "ambari1.mycluster"
a1.vm.network :private_network, ip: "192.168.0.11"
a1.vm.provider :virtualbox do |vb|
vb.memory = "2048"
end
a1.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 8080, host: 8080
a1.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 80, host: 80
end
# Master1
config.vm.define :master1 do |m1|
m1.vm.hostname = "master1.mycluster"
m1.vm.network :private_network, ip: "192.168.0.12"
m1.vm.provider :virtualbox do |vb|
vb.memory = "4096"
end
end
# Slave1
config.vm.define :slave1 do |s1|
s1.vm.hostname = "slave1.mycluster"
s1.vm.network :private_network, ip: "192.168.0.21"
s1.vm.provider :virtualbox do |vb|
vb.memory = "2048"
end
end
# Slave2
config.vm.define :slave2 do |s2|
s2.vm.hostname = "slave2.mycluster"
s2.vm.network :private_network, ip: "192.168.0.22"
s2.vm.provider :virtualbox do |vb|
vb.memory = "2048"
end
endStep 5 - Start the Machines and Install Ambari Server
Vagrant will automatically run the provision defined in Vagrantfile by Shell Provisioner to start the Ambari server machine from Vagrant. And then SSH to the Ambari server
$ vagrant up ambari1 $ vagrant ssh ambari1
As a root user, run the below commands
# Install wget -nv http://public-repo-1.hortonworks.com/ambari/centos6/2.x/updates/2.2.2.0/ambari.repo -O /etc/yum.repos.d/ambari.repo yum -y install ambari-server sudo service ntpd start # Setup. There are several options to configure during setup. ambari-server setup # Start Ambari Server ambari-server start
Add the following FQDN to each the /etc/hosts file on each VM.
192.168.0.11 ambari1.mycluster ambari1 192.168.0.12 master1.mycluster master1 192.168.0.21 slave1.mycluster slave1 192.168.0.22 slave2.mycluster slave2
Set up a password less SSHing from Ambari Node to all other nodes(VMs)
$ ssh-keygen $ cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub >> ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
Copy the ambari server's public key to other nodes' authorized keys to allow communication later.
Step 6 - Deploy HDP Cluster
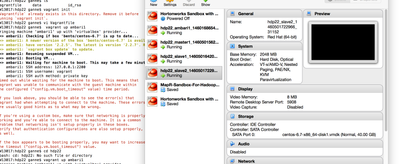
We are ready to deploy a HDP cluster from Ambari Web UI. Because the UI is really simple, I would omit the screenshots here.
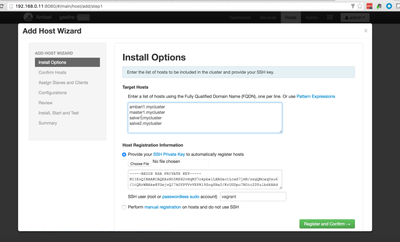
- Access http://192.168.0.11:8080/ from your laptop. The username and password is admin and admin respectively.
- Give a cluster name.
- Select the latest HDP version
- Input hostname of the VMs (one per line) and the SSH private key of Ambari server. SSH user should be
vagrant.
- Accept the default options for rest of the wizard.
- Complete the wizard. It takes about 30m to finish up.
Now we are all set and a 4 nodes HDP cluster ready on your local machine!
Created on 06-17-2016 03:15 PM
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Step 5 installs Ambari 1.7 which is an older version. You should use this step to get the latest version (Ambari 2.2.20):
wget -nv http://public-repo-1.hortonworks.com/ambari/centos6/2.x/updates/2.2.2.0/ambari.repo -O /etc/yum.repos.d/ambari.repo
Created on 06-17-2016 03:29 PM
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
In step 3, the script in the VagrantFile could include:
sudo service ntpd start
The chkconfig command will ensure ntpd starts on bootup. However, I found ntpd did not auto start the first time the instance was brought up with Vagrant. Subsequent boots of the VM work properly.
Created on 06-20-2016 08:52 PM
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Thanks for letting me know this.