Community Articles
- Cloudera Community
- Support
- Community Articles
- Static edge node setup before cluster deployed wit...
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
Created on 10-09-2019 08:56 AM
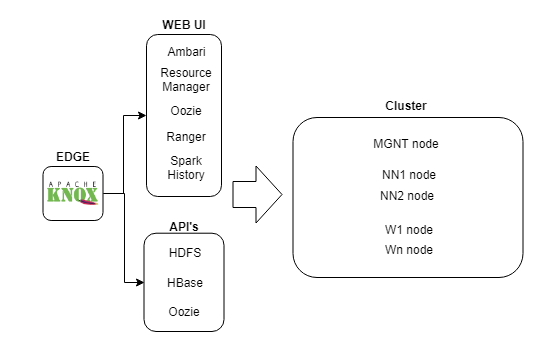
This article will explain how to setup a static edge node as an entry point to a Hadoop cluster deployed using Cloudbreak.
This setup it's not supported by default, because it's not possible to join external vm's in a cluster deployed with Cloudbreak, but in the next article you will find the steps in order to do it.
Cloudbreak is a manager/operator tool to deploy clusters that provides some extra features like scaling, start/stop resources etc in a simple UI. It's a good tool that is growing and sometimes could be a bit rigid and for some core changes on the cluster you will need to deploy a new cluster, for example to change the type of VM or change the HDP version etc.
For this reason in our case we decided to setup a static IaaS virtual machine as edge node, that give us a single and immutable entry point to the cluster, this will never change even we will deploy a new cluster. With this and Knox server we have the ability to deploy a new cluster and then make the switch without deliver again the new URL's and API's to the users.
We will divide the article in three parts:
- How to join the edge node in the cluster
- How to install Knox server in the edge node
- How to add the hostname resolution in the edge node
Join the edge node to the cluster
The first that we need to do is join the edge node in the cluster using Ambari in order to have all the configurations and clients as well.
All the next steps will be performed in the edge node.
- Create the Ambari repo in the edge (you can copy it from another node).
[AMBARI.2.6.2.2]
name=Ambari 2.6.2.2
baseurl=http://xxxx/repo/hdp-repository/ambari/centos7/2.6.2.2/
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=http://xxxx/repo/hdp-repository/ambari/centos7/2.6.2.2/RPM-GPG-KEY/RPM-GPG-KEY-Jenkins
enabled=1
priority=1 - Install the Ambari Agent
yum install ambari-agent
- Update the Ambari Agent configuration to point to the Ambari Server.
vim /etc/ambari-agent/conf/ambari-agent.ini
[server]
hostname="ambari manager server FQDN"
[security]
force_https_protocol=PROTOCOL_TLSv1_2 - In our case we had some errors regarding the https security, we have https enabled and all the VMs isolated from public network, so in order to skip the error we disabled the certificate verification on python.
vim /etc/python/cert-verification.cfg
[https]
verify=disable - Start Ambari Agent service.
ambari-agent start
- Add the edge host in Ambari. Go to Ambari server UI > Add Host and select "Perform manual registration".
- If any warning appears in the host checks, don't skip it, fix it using the HostCleanup script as suggested, if not it will not work.
sudo python "/usr/lib/ambari-agent/lib/ambari_agent/HostCleanup.py" --skip=users
- Finally you will see the new host added in the hosts tab on Ambari UI.
Install Knox on the edge node
We will need a Knox server running in the edge node in order to redirect the UI's and API's from the edge to the current cluster.
To setup Knox follow the next steps using Ambari:
- Go to Ambari UI and then add Knox server on the edge node.
- Configure the topology files to point to the cluster services. Suggestion, copy the default topology under "/etc/knox/2.6.5.0-292/0/topologies/" and rename it with your topology file and fill the correct url's.
- Enable the LDAP cache to speed up the connections.
- In case that you have HTTPS enabled on Ambari Server you will need to install the certificate from Ambari server on the java keystore in the edge node; this is required for the handshake between the edge node and Ambari server.
Test
After Knox installation and setup, you should be able to access to Ambari UI through Knox URL, or use the WEBHDFS API. This URL depends on your configuration:
| EdgeFQDN | Fully qualified domain name of edge node |
| Gateway Path | Knox property in Ambari > Knox > Config (Suggestion set the environment there ie "prod"). |
| Topology | Name of topology file that contains the url's |
- Ambari: https://edgeFQDN:8443/gatewayPath/topology/ambari/#/login
- WEBHDFS: https://edgeFQDN:8443/gatewayPath/topology/webhdfs/v1/?op=LISTSTATUS
Hostname resolution on edge node
This is the core issue that we found when we performed the setup, the previous steps was just the prerequisites before this: When a job is submitted from the edge node, this fails because the edge node was unable to resolve the hostname/ip of workers. Internally, Cloudbreak/Ambari acts like a DNS and provides this information, but in our case Cloudbreak don't recognize the edge node as a cluster node.
When Cloudbreak is used to deploy a cluster and with auto-scaling capabilities in mind, the servers are not registered on the company DNS (usually this requires manual intervention), the hosts are registered internally in Ambari server and Cloudbreak, this is because the number of workers could increase/decrease in hours (scaling).
If your cluster will be static then, you could register all the nodes of the cluster in your DNS company, but probably you will not use Cloudbreak with this approach.
In order to solve the issue with the hostname resolution, what we did was get the information of Hostnames and IP's from Ambari, and populate the /etc/hosts with this information in the edge node.
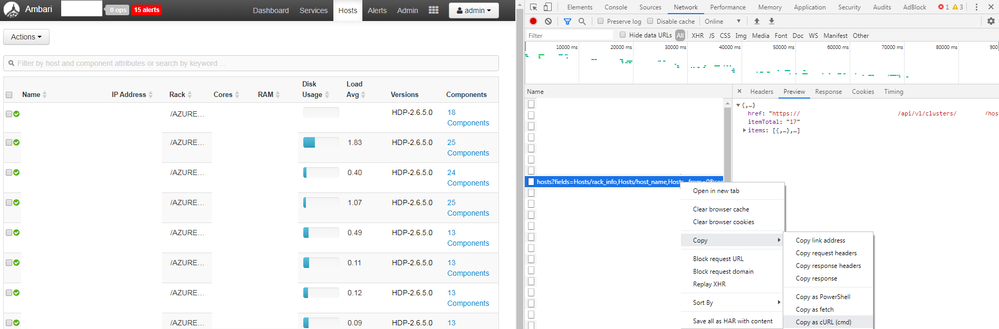
From Ambari UI and hosts tab we can take the API call to list the servers:
This is the full curl:
curl "https://edgeFQDN:8080/api/v1/clusters/clustername/hosts?fields=Hosts/rack_info,Hosts/host_name,Hosts/maintenance_state,Hosts/public_host_name,Hosts/cpu_count,Hosts/ph_cpu_count,Hosts/last_agent_env,alerts_summary,Hosts/host_status,Hosts/last_heartbeat_time,Hosts/ip,host_components/HostRoles/state,host_components/HostRoles/maintenance_state,host_components/HostRoles/stale_configs,host_components/HostRoles/service_name,host_components/HostRoles/display_name,host_components/HostRoles/desired_admin_state,metrics/disk,metrics/load/load_one,Hosts/total_mem,stack_versions/HostStackVersions,stack_versions/repository_versions/RepositoryVersions/repository_version,stack_versions/repository_versions/RepositoryVersions/id,stack_versions/repository_versions/RepositoryVersions/display_name^&minimal_response=true,host_components/logging"
We just want the hostname and IP.
https://edgeFQDN:8443/gatewayPath/gateway/ambari/api/v1/clusters/clustername/hosts?fields=Hosts/host_name,Hosts/ip
With this curl and some transformations we will fix the issue.
JQ Installation
We will need to parse the output of this API call in order to populate the /etc/hosts, for this we will need JQ.
sudo yum install jq
Ambari user setup
We will create an user with "operator" role in order to execute the API call.
- Go to Ambari UI > Manage Ambari > Users > Create User
- Then Roles > Service Operator > add here.
Automation
In the edge node, with user root for example, create a script in order to get the result from API and overwrite the hosts file.
vim curl_ips.sh
#!/bin/bash
curl -u operator:'****' -ks 'https://edgeFQDN:8443/gatewayPath/gateway/ambari/api/v1/clusters/clustername/hosts?fields=Hosts/host_name,Hosts/ip' | jq -r '.items[].Hosts |[ .ip, .host_name, .host_name] | @csv' | sed -e 's/.domain"$//' | sed 's/\"//g' | sed 's/,/ /g' > hosts_ambari
cat hosts_ini hosts_ambari > /etc/hosts
chmod 644 /etc/hosts
Create as well a file named "hosts_ini" with the next entries:
#This entries are autopopullated by root crontab.
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
This script executed by crontab will do a merge between this entries (localhost) and the entries received from Ambari.
Finally add the script execution in the root crontab to be executed every 30 minutes for example.
*/30 * * * * curl_ips.sh
With all this steps you will have the file /etc/hosts in the edge node populated with all the nodes from the cluster, and you will be able to submit jobs even you will scale up the cluster.