Community Articles
- Cloudera Community
- Support
- Community Articles
- Using PartitionRecord (GrokReader/JSONWriter) to P...
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
Created on 08-28-2017 08:20 PM - edited 08-17-2019 11:29 AM
Objective
This tutorial walks you through a NiFI flow that utilizes the PartitionRecord processor with GrokReader/JSONWriter controller services to parse the NiFi app log in Grok format, convert to JSON and then group the output by log level (INFO, WARN, ERROR).
Note: The record-oriented processors and controller services were introduced in NiFi 1.2.0. As such, the tutorial needs to be done running Version 1.2.0 or later.
Environment
This tutorial was tested using the following environment and components:
- Mac OS X 10.11.6
- Apache NiFi 1.3.0
PartitionRecord Flow
Template
Import the template: partitionrecord-groktojson.xml
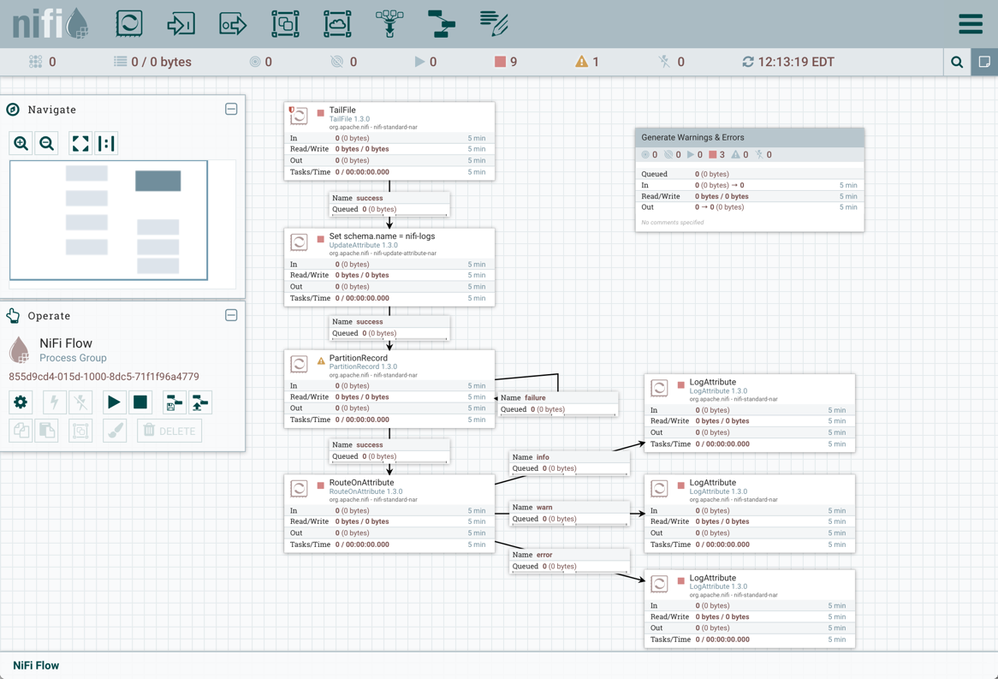
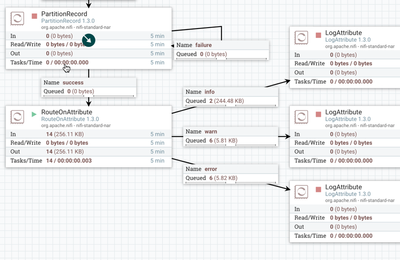
The flow should appear as follows on your NiFi canvas:
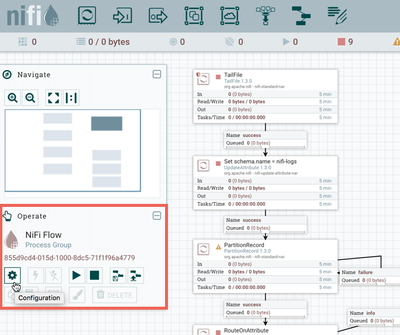
Enable Controller Services
Select the gear icon from the Operate Palette:
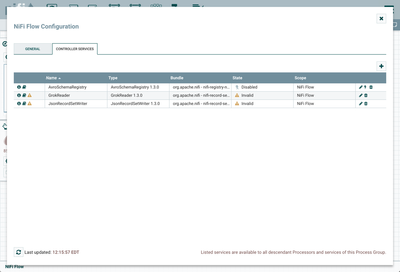
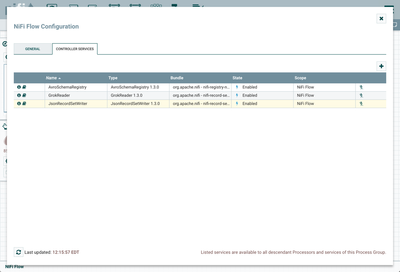
This opens the NiFi Flow Configuration window. Select the Controller Services tab:
Enable AvroSchemaRegistry by selecting the lightning bolt icon/button. This will then allow you to enable the GrokReader and JSONRecordSetWriter controller services. Select the lightning bolt icons for both of these services. All the controller services should be enabled at this point:
The flow is now ready to run.
Flow Overview
Here is a quick overview of the main flow:
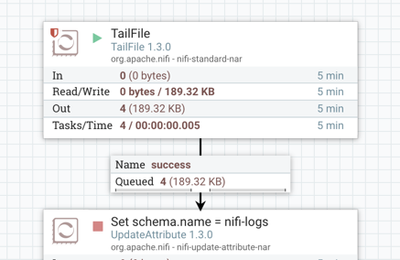
1. TailFile tails the nifi-app.log
2. UpdateAttribute adds Schema Name "nifi-logs" as an attribute to the flowfile
3. PartitionRecord:
- Uses a GrokReader controller service to parse the log data in Grok format. The GrokReader references the AvroSchemaRegistry controller service.
- The AvroSchemaRegistry contains a "nifi-logs" schema which defines information about each record (field names, field ids, field types)
- Uses a JsonRecordSetWriter controller service to write the records in JSON format. The JsonRecordSetWriter references the same AvroSchemaRegistry.
- Groups the records by log level (INFO, WARN, ERROR)
4. RouteOnAttribute sends the data to different connections based on the log level
Flow Details
Generate Warning & Errors
Start the "Generate Warnings & Errors" process group to create sample WARN and ERROR logs.
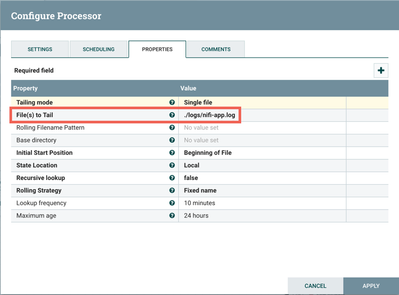
Set schema.name = nifi-logs (TailFile Processor)
This processor is configured to tail the nifi-app.log file:
Start the processor and let it run until multiple flowfiles are generated:
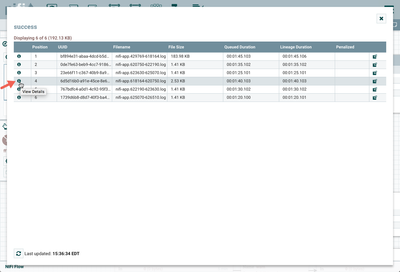
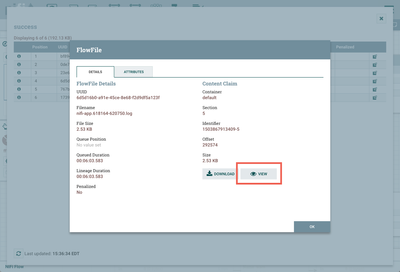
Check to see that flowfiles were generated for info, warning and error logs. Right click on the connection between the TailFile Processor and the UpdateAttribute Processor. In the context menu, select "List Queue" and click the View Details button ("i" icon):
On the Details tab, elect the View button:
to see the contents of one of the flowfiles:
(Note: Both the "Generate Warnings & Errors" process group and TailFile processors can be stopped at this point since the sample data needed to demonstrate the flow has been generated.)
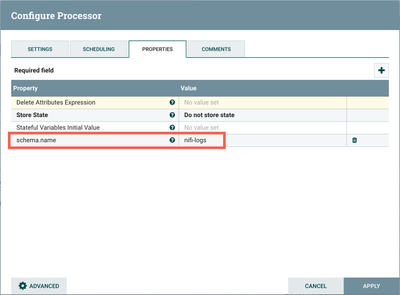
Add Schema Name Attribute (UpdateAttribute Processor)
The next step in the flow is an UpdateAttribute processor which adds the schema.name attribute with the value of "nifi-logs" to the flowfile:
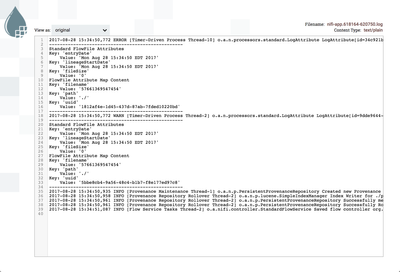
Start the processor, and view the attributes of one of the flowfiles to confirm this:
PartitionRecord Processor
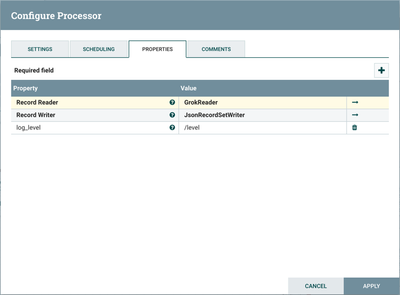
The next processor, PartitionRecord, separates the incoming flowfiles into groups of ‘like’ records by evaluating a user-supplied records path against each record. Looking at the configuration:
Record Reader is set to "GrokReader" and Record Writer is set to "JsonRecordSetWriter". The "GrokReader" controller service parses the log data in Grok format and determines the data's schema. The "JsonRecordSetWriter" controller service determines the data's schema and writes that data into JSON. More details about these controller services can be found below.
A custom record path property, log_level, is used to divide the records into groups based on the field ‘level’.
GrokReader Controller Service
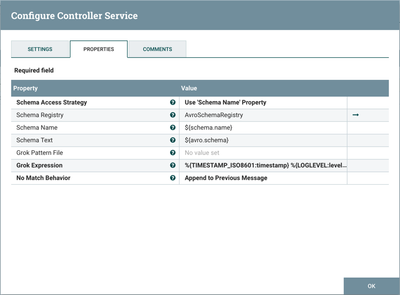
Select the arrow icon next to the "GrokReader" which opens the Controller Services list in the NiFi Flow Configuration. "GrokReader" should be highlighted in the list. Select the View Details button ("i" icon) to see the properties:
With Schema Access Strategy property set to "Use 'Schema Name' Property", the reader specifies the schema expected in an attribute, which in this example is schema.name. The Schema Registry property is set to the AvroSchemaRegistry Controller Service. Grok Expression specifies the format of the log line in Grok format, specifically:
%{TIMESTAMP_ISO8601:timestamp} %{LOGLEVEL:level} \[%{DATA:thread}\] %{DATA:class} %{GREEDYDATA:message}
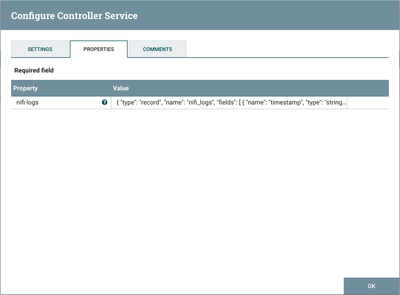
AvroSchemaRegistry Controller Service
The AvroSchemaRegistry defines the "nifi-logs" schema. Select the arrow icon next to "AvroSchemaRegistry" and select the View Details button ("i" icon) to see its properties:
{
"type": "record",
"name": "nifi_logs",
"fields": [
{ "name": "timestamp", "type": "string" },
{ "name": "level", "type": "string" },
{ "name": "thread", "type": "string" },
{ "name": "class", "type": "string" },
{ "name": "message", "type": "string" },
{ "name": "stackTrace", "type": "string" }
]
}
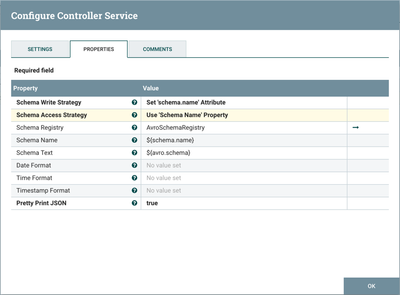
JsonRecordSetWriter Controller Service
Close the window for the AvroSchemaRegistry. Select the View Details button ("i" icon) next to the "JsonRecordSetWriter" controller service to see its properties:
Schema Write Strategy is set to "Set 'schema.name' Attribute", Schema Access Strategy property is set to "Use 'Schema Name' Property" and Schema Registry is set to AvroSchemaRegistry.
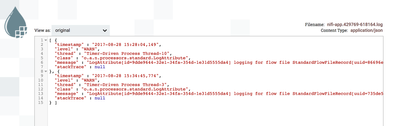
Start the PartitionRecord processor. Looking at the contents of a flowfile, confirm that it only contains logs of one log level. For example, here is a flowfile containing only warnings:
RouteOnAttribute Processor
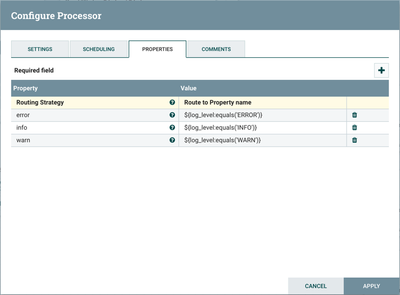
A RouteOnAttribute processor is next in the flow. Looking at the properties:
this processor routes the flowfiles to different connections depending on the log_level (INFO, WARN, ERROR).
Run the RouteOnAttributeProcessor to see this in action:
Helpful Links
Here are some links to check out if you are interested in more information on the record-oriented processors and controller services in NiFi:
- Convert CSV to JSON, Avro, XML using ConvertRecord (Apache NiFi 1.2+)
- Installing a local Hortonworks Registry to use with Apache NiFi
- Running SQL on FlowFiles using QueryRecord Processor (Apache NiFi 1.2+)