Community Articles
- Cloudera Community
- Support
- Community Articles
- Automated provisioning of HDP for Data Governance ...
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
Created on 05-18-2018 12:57 AM - edited 08-17-2019 07:28 AM
Continuing with the theme of one-click installs from the last post, this time we will see how one can provision an HDP 2.6.4 cluster equipped with features for data governance and security through Apache Atlas and Apache Ranger using Cloudbreak in private/public cloud, again of course, with a single command!
To begin with, you’d need:
- Access
to a supported cloud provider (AWS, Azure, GCP, OpenStack) with following resources
configured / identified for the cluster deployment:
- Region / Availability zone
- Virtual Private Network / Security Group
- VM types / sizes identified for master and worker roles
- SSH keypair
- Access to a Hortonworks Cloudbreak instance setup with credentials for the cloud provider(s) of choice [eg: OpenStack, AWS]
- Cloudbreak CLI installed on your machine, in path and configured pointing to the Cloudbreak instance above
You can use this tool to setup Cloudbreak with CLI configured locally on your workstation with just a couple of commands.
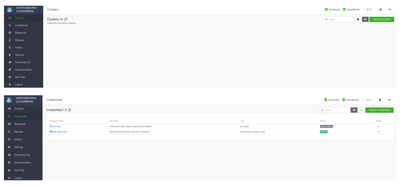
Once this is done, you should have your Cloudbreak instance setup with the credentials as follows:
You should also be able to use the Cloudbreak CLI to talk to the Cloudbreak instance and in turn the cloud provider with their respective credentials.
Now, clone this repo.
Update cloud configurations under:
cloudbreak/clusters/aws/hwx/hwx-aws-dm.json for AWS cloudbreak/clusters/openstack/hwx-field-cloud/hwx-os-dm.json for OpenStack
especially:
general.credentialName // credential to use as configured in Cloudbreak tags // tags for billing, ops and audit placement // region and availability zone network // configured virtual private network instanceGroups.template.instanceType // instance types instanceGroups.template.securityGroup // configured security group associated with the network stackAuthentication // configured SSH key details
Setup Cloudbreak and Create Cluster
If running for the first time, run:
./scripts/import-artifacts-n-create-cluster.sh <CLOUD> [where CLOUD => 'openstack' or 'aws']
This will first import the blueprint (under cloudbreak/blueprints) and recipes (under cloudbreak/recipes) into Cloudbreak and then create the cluster
If the blueprints and recipes have already been imported, run:
./scripts/create-cluster.sh <CLOUD>
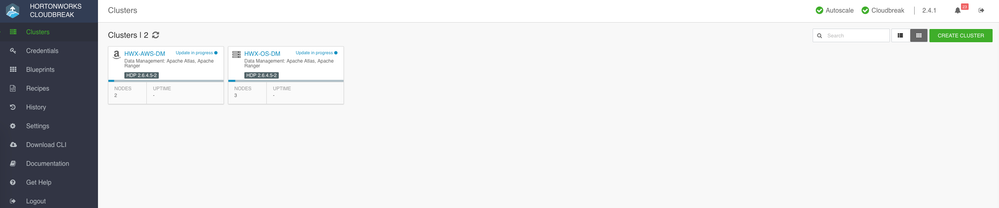
You should now see the cluster being provisioned ...
I also initiated provisioning of the cluster in AWS
./scripts/create-cluster.sh aws
After about 15-20 mins …
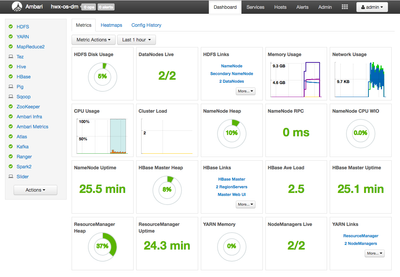
You have HDP clusters setup with Atlas, Ranger and their dependencies including HBase and Kafka all equipped with features for data governance and security!!
A quick peek behind the scenes!
The bulk of the provisioning automation is done through the Ambari blueprint. In this case, cloudbreak/blueprints/hdp26-data-mgmnt.json
One of the first steps and provisioning script does is import this custom Ambari blueprint into Cloudbreak using the CLI - visible in the catalog alongside 3 built-in ones.
Ambari blueprints are the declarative definition of your clusterdefining the host groups and which components to install on which host group. Ambari uses them as a base for your clusters.
In general, the blueprint to be used with Cloudbreak should include the following elements:
The blueprint for this setup has 2 host_groups – master and worker for the respective service roles of all the components.
The configurations section of the blueprint defines mostly the non-default override properties for various services especially Atlas and Ranger.
Refer to the docs for more on Ambari support for Ranger and Atlas. You can also look at sample blueprints for shared services.
To automate provisioning of more nuanced clusters, you can manually build the clusters through Ambari installation wizard and export the blueprint. However, the “blueprint_name" is not included in the export. You must add it before the blueprint can be used by Cloudbreak. You can use these Gists for exporting and adding blueprint_name to the exported blueprint.
This setup uses Postgres as the RDBMS required to store metadata and state information for Ambari and other services like Hive, Ranger etc. (You can update the blueprint to use other supported RDBMSes).
In order for Ranger to use this Postgres instance, one needs to create a DB and a DB user for Ranger and add authentication information in pg_hba.conf. This is automated using a ‘pre-ambari-start’ recipe under recipes/ranger-db-setup.sh that runs on the Ambari server node group.
Recipes are scripts that run on selected node groups before or after cluster installation to help automate scenarios not handled by Ambari blueprints. See here for more on Cloudbreak recipes.
The provisioning script imported these recipes into Cloudbreak using the CLI, making them available for automation of pre/post cluster install steps.
The 2 other recipes you see are:
ranger-db-setup-aws: The AWS counterpart for the ranger-db-setup recipe with customizations for Amazon Linux image
restart-atlas: Restarts Atlas post install for completion
The last set of artifacts that the provisioning script imports into Cloudbreak are the cluster configurations, in this case, for OpenStack and AWS under:
cloudbreak/clusters/aws/hwx/hwx-aws-dm.json for AWS cloudbreak/clusters/openstack/hwx-field-cloud/hwx-os-dm.json for OpenStack
with the following details:
general.credentialName // credential to use as configured in Cloudbreak tags // tags for billing, ops and audit placement // region and availability zone network // configured virtual private network instanceGroups.template.instanceType // instance types instanceGroups.template.securityGroup // configured security group associated with the network stackAuthentication // configured SSH key details
Once all the artifacts are in place the provisioning script uses the following CLI command to initiate cluster install:
cb cluster create --cli-input-json $config_file --name $cluster_name
To Wrap Up …
Hope you enjoyed the article and see how Apache Ambari and Hortonworks Cloudbreak facilitate devops and automation for provisioning complex Hadoop/Spark clusters equipped with enterprise features for governance, security and operations in public/private cloud environments.